Overview
CSV Workbench is a powerful, privacy-first browser application for validating and managing CSV files. Built with React 19 and powered by WebAssembly validation engines, it provides enterprise-grade CSV validation entirely within your browser. Offline-capable Progressive Web App (PWA) with Service Workers. Requires Chrome 86+ or Edge 86+ on laptop/desktop.
🔒 100% Local Processing
Your data never leaves your device. All validation, editing, and processing happens locally in your browser using the File System Access API.
Key Features
✓ Offline-Capable Architecture
Works without internet connection. Progressive Web App (PWA) with Service Workers.
✓ High-Performance Validation
WebAssembly engines provide high-performance validation with Web Worker background processing.
✓ Automatic Schema Generation
Intelligent type detection creates schemas from your CSV data automatically.
✓ RFC 4180 Strict Compliance
Validates CSV format according to RFC 4180 standard (comma delimiter, double quotes).
✓ Rich Data Types
Six CSV Schema data types: CsvString, CsvInteger, CsvDecimal, CsvMoney, CsvDateTime, CsvBoolean with rich constraints and RFC 3339 datetime support.
✓ Memory-Efficient Processing
Streaming validation with optimized memory usage for efficient processing of large files.
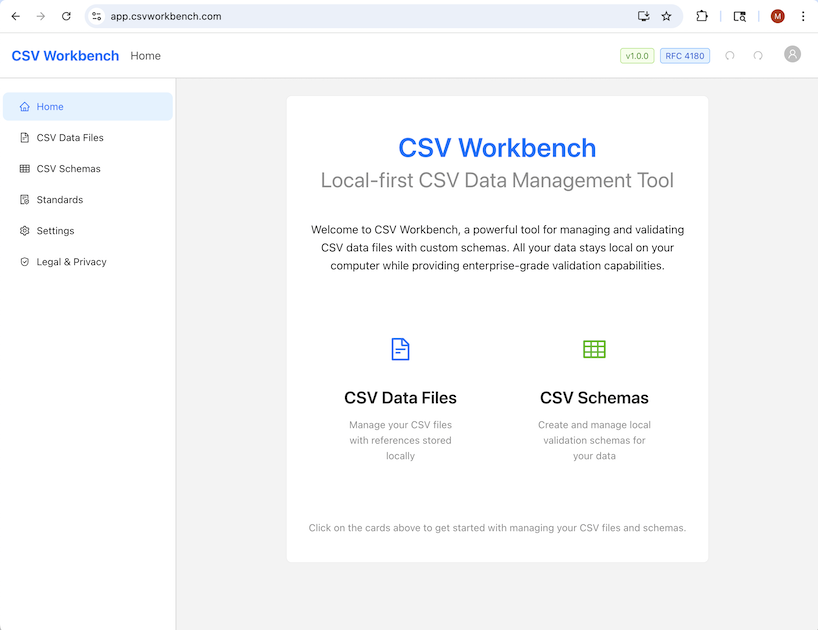
What CSV Workbench Looks Like
Here's a preview of the CSV Workbench interface showing the CSV editor, validation features, and schema management:
Benefits and Use Cases
The CsvSchema framework is a powerful tool for ensuring data quality and consistency. By defining a clear, machine-readable contract for CSV files, it offers significant advantages for both human data handlers and automated systems. Its primary benefits are improved data integrity, accelerated development cycles, and more resilient data-driven systems.
For Data Practitioners
Data practitioners—including analysts, developers, and scientists—can leverage CsvSchema to streamline their workflows and build trust in their data.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Ensure Data Integrity | Establish a single source of truth for data validation. Enforce consistent data types, formats, and structures at the point of ingestion to prevent quality issues from spreading downstream. |
| Accelerate Development | Replace manual, repetitive validation scripts with automated data quality checks. This allows developers to focus on core application logic, reduce boilerplate code, and spend less time debugging. |
| Improve Collaboration | Bridge the gap between data producers and consumers. A CsvSchema acts as clear, executable documentation, creating a shared understanding of data requirements and reducing miscommunication. |
| Diagnose Errors Faster | Pinpoint errors with precision. The validation engine generates detailed, line-specific error reports with structured codes and remediation suggestions, enabling practitioners to resolve issues without manual file inspection. |
| Flexible and Adaptable | Integrate validation anywhere. Use the framework as a command-line tool for ad-hoc file checks or as a library within larger data pipelines, applications, and automated testing suites. |
| Generate Schemas Automatically | Bootstrap schema creation. Automatically generate a baseline schema from existing CSV data to accelerate the definition process and ensure accuracy. |
For Automated Systems
For automated systems such as ETL pipelines and microservices, CsvSchema acts as a critical data quality gatekeeper, ensuring reliability and predictability.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhance System Reliability | Build resilient data pipelines. Act as a defensive gateway that rejects non-compliant data at the entry point, protecting automated workflows from unexpected inputs that cause crashes or silent failures. |
| Protect Downstream Assets | Safeguard data-dependent systems. Prevent malformed or invalid data from corrupting databases, triggering application exceptions, or producing flawed analytics. This is critical for training high-quality AI/ML models. |
| Standardize Data Exchange | Enforce a clear data contract. Standardize data exchange between services by establishing a formal, machine-enforceable contract for any system that consumes CSV files, ensuring predictable and reliable integration. |
| Enable Scalable Processing | Validate data at scale. The engine's high-throughput architecture, featuring streaming, parallel processing, and intelligent optimization, handles large-scale validation without becoming a performance bottleneck. |
| Automate Governance | Automate data governance. Embed governance rules directly into automated workflows. A CsvSchema can enforce compliance with internal standards and external regulations, ensuring data handling meets all required policies. |
| Optimize Performance Automatically | Achieve optimal performance without manual tuning. The performance-optimized validator intelligently selects the best validation strategy (standard, streaming, or parallel) based on file size, system resources, and schema complexity. |
💡 Real-World Impact
Whether you're a data practitioner ensuring quality at the point of ingestion or building automated systems that require reliable data contracts, CSV Workbench provides the tools to transform chaotic CSV files into trustworthy data assets.
Core Components
The CSV Schema validation framework consists of four essential core components that work together to provide comprehensive data validation.
CSV Data File
The CSV file containing data that requires validation of both structure and content.
CSV Schema
A JSON file that defines the validation rules determining what constitutes a valid and compliant CSV Data File.
CSV Schema Meta-Schema
A JSON file that defines the structure of a valid CSV Schema, implemented as a standard JSON schema.
Validation Engine
The core CSV Schema validation engine that orchestrates the entire validation process.
Four User-Facing Validation Operations
The validation framework provides four user-facing validation operations that combine multiple validation steps behind the scenes:
1. Validate CSV File Quality
User Action: Add a CSV file reference to CSV Workbench
What happens automatically:
- Basic CSV file structure validation
- RFC 4180 compliance (comma delimiter, double quote escaping, consistent column counts)
- Security screening (CSV injection protection, binary content detection)
- UTF-8 encoding validation
User Experience: When adding a CSV file reference, the file is automatically validated. If validation fails, you see detailed error information and cannot save the reference until issues are resolved.
2. Validate CSV Schema File Quality
User Action: Add a CSV Schema file reference to CSV Workbench
What happens automatically:
- CSV Schema structural validation (JSON syntax, meta-schema conformance)
- CSV Schema logical validation (column definition logic, constraint compatibility)
User Experience: When adding a schema file reference, the file is automatically validated for both structure and logic. If validation fails, you see detailed error information and cannot save the reference until issues are resolved.
3. Validate CSV Data Using Schema
User Action: Click "Validate Data" button in CSV Data Editor (when a schema is associated with the CSV file)
What happens automatically:
- CSV structural compliance validation (column count, names, order match schema)
- CSV data validation (data types, constraints, required fields, patterns)
User Experience: When validating a CSV file against its associated schema, both structural compliance and data validation occur together. You receive a comprehensive validation report showing all issues found.
4. Generate Schema from CSV File
User Action: Click "Generate Schema" button for a CSV file
What happens automatically:
- Column definitions with inferred data types (6 CSV data types supported)
- Detected constraints (patterns, ranges, formats)
- Required field indicators
- RFC 4180 compliant schema structure
User Experience: When generating a schema, you receive a schema review dialog showing detected column types, confidence levels, and sample values. You can accept the generated schema or edit it before saving.
💡 Validation Workflow
These four operations represent how you interact with CSV Workbench. Behind the scenes, multiple validation steps work together to ensure your data meets quality standards at every stage.
Browser Requirements
CSV Workbench requires modern browser features for optimal performance and security.
⚠️ Supported Browsers
Chrome 86+ and Edge 86+ are the only supported browsers.
Firefox and Safari do not support the File System Access API required for local file operations.
Required Browser Features
- File System Access API - For reading and writing local files
- IndexedDB - For storing file metadata (not file content)
- WebAssembly - For high-performance validation engines
- Web Workers - For background validation processing
- Service Workers - For offline functionality (PWA)
Technical Terms
Understanding these technical terms will help you better understand how CSV Workbench works:
IndexedDB
A browser database for storing structured data locally on your computer. CSV Workbench uses IndexedDB to store file references and metadata (like file names, descriptions, and associations) but never stores your actual CSV file content.
File System Access API
A browser API that allows web applications to read and write files directly on your computer's file system. This enables CSV Workbench to save changes directly to your files without uploading them to a server.
WebAssembly (WASM)
A high-performance binary format that runs in web browsers at near-native speed. CSV Workbench uses WebAssembly for its validation engines to achieve fast validation of large CSV files.
Web Workers
Background threads that run JavaScript code without blocking the user interface. CSV Workbench uses Web Workers to perform validation in the background, keeping the application responsive even when processing large files.
Service Workers
Scripts that run in the background and enable offline functionality by caching application resources. Service Workers allow CSV Workbench to work without an internet connection.
Progressive Web App (PWA)
A web application that can work offline, be installed on your device, and provide an app-like experience. CSV Workbench is a PWA, which means it can function without internet connectivity and can be installed like a native application.
💡 Why These Technologies?
These modern browser technologies work together to enable CSV Workbench to provide enterprise-grade validation entirely in your browser, with complete privacy and security. The File System Access API allows direct file access without uploads, while IndexedDB stores only metadata locally.
First Steps
Get started with CSV Workbench in just a few simple steps.
1. Access the Application
Navigate to app.csvworkbench.com using Chrome 86+ or Edge 86+.
2. Open a CSV File
Click "CSV Data Files" in the left sidebar, then click "Add CSV File Reference". Select a CSV file from your computer. The browser will request permission to access the file.
Automatic Validation: When you add a CSV file, it is automatically validated for RFC 4180 compliance (proper structure, comma delimiters, quote escaping). The validation results are displayed immediately, and the file is only added if it passes validation.
File Permissions: You'll be prompted to grant read/write access. This permission is stored by your browser and allows CSV Workbench to save changes directly to your file.
3. View and Edit Your Data
Once opened, your CSV file appears in an editable table (for files ≤50MB). You can:
- Click any cell to edit its value
- Add new rows or columns
- Delete rows or columns
- Rename column headers
- Move columns left or right
All changes are auto-saved immediately to your local file.
4. Generate or Load a Schema
To validate your data, you need a schema. You can either:
- Generate automatically: Click "Generate Schema from Data" to create a schema based on your CSV
- Load existing: Associate an existing schema file from the "Associated Schema" dropdown
5. Validate Your Data
Once a schema is associated, click "Validate with Schema". The validation runs in a background worker and shows progress. Results appear in a detailed dialog showing:
- Validation status (success/failure)
- Error and warning counts
- Detailed error messages with row/column locations
- Processing time and performance metrics
- Raw JSON response from the validation engine
CSV Folders
CSV Folders is a screen in the left-hand navigation (between Home and CSV Data Files) where you manage the local folders that CSV Workbench may read from and write to. Because the browser's File System Access API requires explicit user approval for every folder, this screen is the single place where you grant, review, and revoke that access.
Why CSV Folders?
The browser's File System Access API requires a user gesture (folder picker) before any local directory can be read or written. CSV Folders gives you a clear, centralized registry of every folder you have authorized, and forms the foundation for future agent-based automation that can operate within those pre-approved locations.
Adding a Folder
- Navigate to CSV Folders in the left sidebar.
- Click "Add Folder".
- The browser's folder picker opens — select the directory you want CSV Workbench to access and grant read/write permission.
- The folder appears in the table with a Granted permission badge.
Folder Table
Each registered folder shows the following columns:
- Display Name — User-editable label for the folder (defaults to the directory name).
- Directory Name — The actual name of the directory on disk (read-only).
- Permission — Current access status: Granted, Needs Permission, or Denied.
- Added — When the folder was first registered.
- Actions — Re-authorize, Edit Name, Remove.
Permission States
| Status | Meaning | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Granted | CSV Workbench has active read/write access. | None. |
| Needs Permission | The browser needs to re-confirm access (e.g., after a browser restart). | Click Re-authorize and approve the browser prompt. |
| Denied | Permission was explicitly declined. | Click Re-authorize to try again, or Remove the folder. |
Folder Actions
- Re-authorize — Appears when permission is Needs Permission or Denied. Triggers the browser permission prompt to restore access.
- Edit Name — Change the display name shown in CSV Workbench. The underlying directory on disk is not affected.
- Remove — Removes the folder from the registry. No files on disk are deleted; CSV Workbench simply forgets the folder.
Browser Restart Behavior
Browsers do not persist file-system permissions across sessions. After restarting Chrome or Edge, folders may show Needs Permission. Use the Re-authorize action to restore access without re-selecting the folder.
Undo / Redo Support
Adding, removing, and renaming folders are all undoable operations. Use Ctrl+Z / Cmd+Z to undo or Ctrl+Y / Cmd+Y to redo. The Undo and Redo buttons in the app header also reflect these operations.
Managing CSV Files
CSV Workbench provides a comprehensive file management system for your CSV files.
Opening Files
Navigate to CSV Data Files and click "Add CSV File Reference". The browser's file picker will open, allowing you to select a CSV file from your computer.
✓ Automatic Validation on Add
When you add a CSV file, CSV Workbench automatically performs Basic CSV Validation to check the file's structure and RFC 4180 compliance before adding it to your workspace. The validation results are displayed immediately, and the file is only added if validation succeeds.
File References: CSV Workbench stores a reference to your file (not the content) in IndexedDB. This allows quick access to recently opened files without re-selecting them.
File List View
The CSV Data Files view shows all your opened files with:
- File Name - The name of your CSV file
- Size - File size in KB/MB/GB
- Associated Schema - Which schema (if any) is linked to this file
- Last Accessed - When you last opened this file
- Actions - Edit, validate, or remove the file reference
File Metadata
You can add descriptions and notes to your files for better organization. Click the "Edit Information" button in the CSV Data Editor to add:
- Description - A brief description of the file's purpose
- Notes - Additional notes or context
Removing File References
If a file is no longer needed or has been moved/deleted, you can remove its reference from CSV Workbench. This only removes the reference - it does not delete the actual file from your computer.
Missing Files: If you try to open a file that has been moved or deleted, CSV Workbench will detect this and offer to remove the reference.
Editing Data
CSV Workbench provides powerful editing capabilities using the File System Access API for direct file operations.
⚠️ File Size Limits
Files ≤50MB: Fully editable with all rows loaded
Files >50MB: Read-only preview mode (first 200 rows). Validation still runs on the complete file.
Editing Cells
Click any cell to open the edit dialog. You can:
- Edit single-line or multi-line text values
- View the current row and column information
- See validation errors for that cell (if any)
Changes are saved immediately when you click "Save".
Adding and Deleting Rows
Use the "Add Row" button to insert a new row. Fill in values for each column, then click "Add Row" to save. The new row is appended to the end of your CSV file.
To delete rows, select them using the checkboxes and click "Remove Selected". You can also delete individual rows using the delete button in the Actions column.
Managing Columns
Column operations include:
- Add Column: Click "Add Column" to insert a new column with an optional default value
- Rename Column: Click the edit icon next to any column header to rename it
- Move Column: Select a column by clicking its header, then use "Move Column Left/Right" buttons
Auto-Save
All changes are automatically saved to your local file immediately. You'll see a confirmation message when changes are saved successfully.
No Manual Save Required: CSV Workbench automatically writes changes to your file as you make them, ensuring your work is never lost.
Schema Management
Schemas define the structure and validation rules for your CSV files.
Creating Schemas
There are three ways to create a schema:
- Auto-Generate: Click "Generate Schema from Data" in the CSV Data Editor to automatically create a schema based on your CSV file's structure and data patterns
- Manual Creation: Navigate to "CSV Schemas" and click "Create New Schema" to build a schema from scratch
- Add Existing Schema: Navigate to "CSV Schemas" and click "Add Schema Reference" to add an existing schema file from your computer
✓ Automatic Validation on Add
When you add an existing schema file, CSV Workbench automatically performs Basic Schema Validation to check the schema's structure and compliance before adding it to your workspace. The validation results are displayed immediately, and the file is only added if validation succeeds.
Editing Schemas
The Schema Editor provides a comprehensive interface for defining validation rules:
- Basic Information: Name, version, description, and notes
- Column Definitions: Add, edit, or remove columns with specific data types and constraints
- Governance Fields: Author, contact, business owner, technical owner, documentation links
- Settings: First row header, allow additional columns, meta schema version
Column Configuration
For each column, you can specify:
- Name: Column identifier (case-sensitive option available)
- Data Type: CsvString, CsvInteger, CsvDecimal, CsvMoney, CsvDateTime, CsvBoolean
- Required: Whether the column must be present and contain data
- Constraints: Type-specific validation rules (length, range, format, patterns)
- Description: Documentation for the column's purpose
Schema Validation
Click "Validate Schema" to check your schema for errors before using it. The validation engine checks for:
- Required fields (name, version)
- Duplicate column names
- Invalid constraint combinations
- Schema structure compliance
Associating Schemas with CSV Files
In the CSV Data Editor, use the "Associated Schema" dropdown to link a schema to your CSV file. Once associated, you can validate the CSV data against the schema's rules.
Validation
CSV Workbench provides four user-facing validation operations powered by WebAssembly engines. Each operation combines multiple validation steps to ensure data quality.
💡 Understanding Validation Operations
These operations represent how you interact with validation in CSV Workbench. Some run automatically when you add files, while others are triggered manually. See the Core Components section for detailed information about each operation.
Validation Operations
1. Validate CSV File Quality
Trigger: Automatically when adding a CSV file reference
Validates CSV structure and RFC 4180 compliance:
- Basic CSV file structure
- RFC 4180 compliance (comma delimiter, double quotes, consistent columns)
- Security screening (CSV injection, binary content)
- UTF-8 encoding validation
Result: Pass/fail with specific structural or security issues identified. File reference cannot be saved until validation passes.
2. Validate CSV Schema File Quality
Trigger: Automatically when adding a CSV Schema file reference
Validates schema structure and logic:
- JSON syntax and meta-schema conformance
- Required fields presence and proper data types
- Column definition logic and constraint compatibility
- Cross-field dependencies and business rule consistency
Result: Pass/fail with JSON schema validation errors or logical inconsistencies. Schema reference cannot be saved until validation passes.
3. Validate CSV Data Using Schema
Trigger: Manually via "Validate Data" button (requires associated schema)
Validates CSV data against schema rules:
- Structural compliance (column count, names, order match schema)
- Data type compliance for each cell
- Constraint validation (length, range, format, patterns)
- Required field presence and custom validation rules
Result: Comprehensive validation report with row/column-specific errors, severity levels, and remediation suggestions.
4. Generate Schema from CSV File
Trigger: Manually via "Generate Schema" button
Automatically generates a CSV Schema from CSV data:
- Column definitions with inferred data types (6 types supported)
- Detected constraints (patterns, ranges, formats)
- Required field indicators
- RFC 4180 compliant schema structure
Result: Schema review dialog showing detected types, confidence levels, and sample values. Accept or edit before saving.
Running Validation
Validation runs in a Web Worker to keep the UI responsive. For large files, you'll see:
- Progress indicator: Shows percentage complete and current phase
- Row counter: Displays rows processed vs. total rows
- Performance metrics: Processing time
Understanding Results
Validation results include:
- Status: Success or failure
- Error Count: Number of critical errors found
- Warning Count: Number of warnings (non-critical issues)
- Error Details: Each error shows row number, column name, value, and suggested fix
- Raw JSON: Complete response from the validation engine for debugging
💡 File Size Support
Files ≤50MB are fully editable. Files >50MB show a read-only preview of the first 200 rows but validation still runs on the complete file using streaming validation with Web Workers.
Data Types
CSV Workbench supports six data types as defined in CSV Schema version 1.0, each with rich constraint options.
CsvString
String data type with pattern matching and comprehensive text constraints.
Constraints:
- Pattern Matching: PCRE-compatible regex patterns
- Simple Constraints: BeginsWith, EndsWith, Contains, NotContains
- Length: MinLength, MaxLength
- Value Lists: AllowedValues, ForbiddenValues
- Character Controls: AllowUnicode, AllowWhitespace, AllowControlCharacters, AllowLineBreaks
- Case Sensitivity: Configurable case sensitivity
CsvInteger
Integer data type with 64-bit range support.
Constraints:
- AllowNegative: Flag to permit negative values
- Range: InclusiveMin, InclusiveMax
- Support: 64-bit integer range
CsvDecimal
Decimal number data type with precision control and flexible formatting.
Constraints:
- AllowNegative: Flag to permit negative values
- Decimal Separator: PERIOD or COMMA
- Thousands Separator: COMMA, PERIOD, SPACE, NONE, THIN_SPACE, NON_BREAKING_SPACE, APOSTROPHE
- Precision: MaxDecimalPlaces
- Range: InclusiveMin, InclusiveMax, ExclusiveMin, ExclusiveMax
CsvMoney
Currency data type with comprehensive ISO 4217 support, extensive currency symbol recognition, flexible formatting options, and enhanced validation for real-world currency data.
Core Features:
- ISO 4217 Currency Codes: Full support for all standard currency codes with improved validation (USD, EUR, GBP, JPY, CHF, CAD, AUD, CNY, INR, and 150+ more)
- Extensive Currency Symbol Support: Comprehensive recognition of currency symbols including $, €, £, ¥, ₹, ₽, ₩, ₪, ₱, ₦, ₴, ₡, ₵, ₲, ₸, ₺, ₼, ₾, ₿, and many more regional symbols
- Improved Currency Code Validation: Enhanced validation ensures currency codes are valid ISO 4217 codes and properly formatted
- Symbol-Code Matching: Validates that currency symbols correctly correspond to the specified currency code
- Flexible Format Support: Multiple format options for different regional and business requirements
- Whitespace Handling: Intelligent parsing with optional whitespace between currency indicators and amounts
Format Options:
- CODE_AMOUNT: Currency code before amount (e.g.,
USD 1,234.56,EUR 1.234,56) - AMOUNT_CODE: Amount before currency code (e.g.,
1,234.56 USD,1.234,56 EUR) - SYMBOL_AMOUNT: Currency symbol before amount (e.g.,
$1,234.56,€1.234,56,£1,234.56) - AMOUNT_SYMBOL: Amount before currency symbol (e.g.,
1,234.56$,1.234,56€) - AMOUNT_ONLY: Numeric amount without currency indicator (e.g.,
1,234.56)
Numeric Constraints:
- AllowNegative: Flag to permit negative values with proper sign handling
- Decimal Separator: PERIOD or COMMA (region-specific)
- Thousands Separator: COMMA, PERIOD, SPACE, NONE, THIN_SPACE, NON_BREAKING_SPACE, APOSTROPHE
- Precision: MaxDecimalPlaces for controlling decimal precision
- Range Validation: InclusiveMin, InclusiveMax, ExclusiveMin, ExclusiveMax
Enhanced Validation Features:
- Format Consistency: Ensures all values in a column follow the same format pattern
- Improved Currency Code Validation: Verifies currency codes against the complete ISO 4217 standard with enhanced error detection
- Comprehensive Symbol Recognition: Validates currency symbols from a comprehensive database covering major and regional currencies worldwide
- Symbol-Code Correspondence: Ensures currency symbols match the specified currency code (e.g., $ must be used with USD, € with EUR)
- Whitespace Flexibility: Handles optional spaces between currency indicators and amounts
- Sign Position Validation: Ensures negative signs are in correct positions for the format
- Separator Consistency: Validates proper use of decimal and thousands separators
- Multi-Character Symbol Support: Handles both single-character (e.g., $, €) and multi-character currency symbols
CsvDateTime
Date and time data type with comprehensive ISO 8601 and RFC 3339 support, flexible format options, and timezone handling.
Supported Standards:
- ISO8601_DATE: Date-only format (
YYYY-MM-DD) - ISO8601_DATETIME: Local datetime (
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS) - ISO8601_DATETIME_UTC: UTC datetime (
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ) - ISO8601_DATETIME_OFFSET: RFC 3339 compliant with timezone offset
- CUSTOM: Rust strftime patterns
Key Features:
- Automatic format detection for ISO 8601 variants
- Leap year validation and date existence checks
- Strict IANA Time Zone Database validation
- Flexible parsing modes (AllowPartial, StrictParsing)
- Fractional seconds with nanosecond precision
CsvBoolean
Boolean data type with configurable true/false representations.
Constraints:
- True Values: Configurable (e.g., "true", "yes", "1", "Y")
- False Values: Configurable (e.g., "false", "no", "0", "N")
- Case Sensitivity: Separate settings for True and False values
💡 CSV Schema Version 1.0
All data types are defined in the CSV Schema specification version 1.0. The schema provides a standardized way to validate CSV data with type safety and rich constraints.
DateTime Validation
CSV Workbench provides comprehensive ISO 8601 and RFC 3339 datetime validation with flexible format support and timezone handling.
✓ Standards Compliance
- RFC 3339 Compliant for
ISO8601_DATETIME_OFFSETvariant - ISO 8601 Compatible for DATE, DATETIME, and DATETIME_UTC variants
- Custom Pattern Support for locale-specific formats
ISO 8601 vs RFC 3339
Understanding the relationship between these standards is crucial for proper datetime validation:
ISO 8601
Broad international standard with many format options:
- Multiple date formats allowed
- Flexible separators (T or space)
- Various timezone formats
- Reduced precision permitted
RFC 3339
Strict profile for Internet protocols:
- Only
YYYY-MM-DDformat - Only T separator required
- Only Z or ±hh:mm timezones
- Full precision required
💡 Key Principle
RFC 3339 is a strict subset of ISO 8601. Every valid RFC 3339 timestamp is an ISO 8601 timestamp, but not every ISO 8601 timestamp is valid under RFC 3339.
Supported DateTime Formats
The validation engine automatically detects and validates four ISO 8601 variants:
1. ISO8601_DATE
Format: YYYY-MM-DD
Example: 2024-01-15
Validation: Custom validation with leap year logic, month range (1-12), and day range based on month and leap year calculations.
Use Case: Date-only fields (birth dates, effective dates, etc.)
2. ISO8601_DATETIME
Format: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS (local datetime, no timezone)
Example: 2024-01-15T10:30:00
Validation: Validates date and time components, rejects timezone suffixes.
Supports partial time precision with AllowPartial: true.
Use Case: Local times without timezone context (appointment times, schedules)
3. ISO8601_DATETIME_UTC
Format: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ (UTC datetime with 'Z' suffix)
Example: 2024-01-15T10:30:00Z
Validation: Requires 'Z' suffix, validates date and time components.
Supports partial time precision with AllowPartial: true.
Use Case: UTC timestamps (logs, events, API responses)
4. ISO8601_DATETIME_OFFSET
Format: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS±HH:MM (datetime with timezone offset)
Example: 2024-01-15T10:30:00+05:00
Validation: Full RFC 3339 compliance with comprehensive datetime parsing. Requires timezone offset (+HH:MM or -HH:MM), supports fractional seconds.
Use Case: Timezone-aware timestamps (international events, distributed systems)
Date Validation Features
✓ Leap Year Validation
Accurate leap year calculations:
- ✅
2024-02-29(2024 is leap year) - ❌
2023-02-29(2023 is not) - ✅
2000-02-29(divisible by 400) - ❌
1900-02-29(divisible by 100 but not 400)
✓ Month & Day Validation
Validates date existence:
- Month range: 1-12
- 31 days: Jan, Mar, May, Jul, Aug, Oct, Dec
- 30 days: Apr, Jun, Sep, Nov
- 28/29 days: Feb (leap year dependent)
Time Component Validation
- Hour: Range 0-23 (24-hour format)
- Minute: Range 0-59
- Second: Range 0-59
- Fractional Seconds: Supported with nanosecond precision (e.g.,
10:30:00.123)
Timezone Support
The validation engine strictly enforces IANA Time Zone Database IDs in schemas.
- IANA IDs Only: Must use canonical IDs like
America/New_York,Europe/London,Asia/Tokyo. - UTC: Use
UTC. The schema validation rejectsZandGMT(thoughZis accepted in data values for offsets). - No Abbreviations: Abbreviations like
PST,CET,ESTare rejected to prevent ambiguity. - Schema-Time Validation: Invalid timezones are caught when you validate the schema itself.
Flexible Parsing Modes
AllowPartial
When enabled, accepts partial time precision:
2024-01-15T10Z(hour only)2024-01-15T10:30Z(hour and minute)2024-01-15T10:30:00Z(full precision)
StrictParsing
When enabled (default), enforces:
- Full
HH:MM:SSformat (unless AllowPartial) - Exact format matching
- No lenient parsing
Custom Pattern Support
When using Standard: CUSTOM, patterns MUST use Rust strftime syntax.
Common supported specifiers:
| Pattern | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
%Y-%m-%d |
ISO date | 2024-01-15 |
%d/%m/%Y |
Day-first (European) | 15/01/2024 |
%m/%d/%Y |
Month-first (US) | 01/15/2024 |
%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S |
Datetime with seconds | 2024-01-15 10:30:00 |
Validation Architecture
The validation uses a two-phase approach for optimal performance:
Phase 1: Fast-Path
Quick format checks:
- String length validation
- Separator character checks
- Basic numeric range validation
- Timezone suffix detection
Phase 2: Full Validation
Detailed parsing with chrono:
- Complete date/time parsing
- Leap year validation
- Date existence checks
- Timezone offset parsing
DateTime Error Codes
The validation engine emits specific error codes for different validation failures:
Schema Validation Errors (Caught when editing schema)
- SCHEMA_DATETIME_JAVA_PATTERN_DETECTED: Pattern uses unsupported syntax. Remediation: Use strftime syntax (e.g.,
%Y-%m-%d). - SCHEMA_DATETIME_INVALID_PATTERN_SYNTAX: Pattern contains invalid strftime specifiers.
- SCHEMA_DATETIME_INVALID_TIMEZONE: Timezone is not a valid IANA ID (e.g.,
PST). Remediation: UseAmerica/Los_Angeles.
Data Validation Errors (Caught when validating CSV)
- DATETIME_INVALID_FORMAT: Value doesn't match expected ISO8601 variant
- DATETIME_PATTERN_MISMATCH: Value doesn't match custom pattern
- DATETIME_INVALID_DATE: Non-existent date (e.g., Feb 30, invalid leap year)
- DATETIME_UNSUPPORTED_STANDARD: Unsupported datetime standard specified
💡 Implementation Details
DateTime validation is powered by high-performance WebAssembly engines for fast, reliable validation. The implementation provides 100% test coverage for all datetime error codes and edge cases including leap years, timezone handling, and format variations.
Large Files
CSV Workbench handles large files efficiently with specialized processing modes.
File Size Thresholds
≤50MB - Full Edit Mode
- All rows loaded and editable
- Full table navigation
- Add/edit/delete operations
- Column management
- Auto-save to local file
>50MB - Preview Mode
- First 200 rows displayed (read-only)
- Preview mode only
- Full validation runs on complete file
- No editing capabilities
- File System Access API for direct access
Validation Performance
Validation is optimized for performance:
- Memory-efficient streaming validation
- Real-time progress updates during validation
- Runs in Web Worker to keep UI responsive
- Works completely offline with PWA capabilities
✓ Best Practices
- Close other browser tabs to free up memory during validation
- Allow validation to complete without interruption
- Use Chrome 86+ or Edge 86+ for best performance
- Ensure stable browser environment during large file operations
Keyboard Shortcuts
CSV Workbench provides keyboard shortcuts for efficient navigation and operations.
Global Shortcuts
Mac Users: Use Cmd instead of Ctrl for all shortcuts.
Appearance & Themes
CSV Workbench supports configurable themes so you can match the interface to your environment and accessibility needs. Theme changes apply instantly and are preserved for future sessions.
Theme Modes
- Light: Standard light theme optimized for clarity and readability.
- Dark: Low‑light friendly theme that reduces glare.
- High Contrast: Increased contrast and clearer boundaries for improved legibility.
- System: Follows your operating system preference (Light or Dark) and honors high‑contrast settings when enabled.
Your theme preference is stored locally in your browser and never transmitted. Changing themes does not modify your CSV data.
How to Change the Theme
- Open Settings in the left sidebar.
- In Appearance, choose Light, Dark, High Contrast, or System.
- The UI updates immediately across all screens.
System Mode Details
System mode automatically tracks your OS appearance. When your OS switches between Light and Dark, CSV Workbench follows. If your OS high‑contrast setting is enabled, high‑contrast styling is applied where available.
Accessibility
- High Contrast mode increases color contrast and adds clearer borders and focus indicators.
- Theme choices are compatible with keyboard navigation and screen readers.
Database Reset
CSV Workbench provides a database reset feature to clear all stored metadata and return the application to its default state.
⚠️ Important: Your Files Are Safe
Database reset only clears metadata stored in IndexedDB. Your actual CSV and schema files on disk are NOT affected and remain completely safe.
What Gets Cleared
The database reset operation removes the following metadata from IndexedDB:
- CSV File References: Pointers to your CSV files (not the actual files)
- Schema File References: Pointers to your schema files (not the actual files)
- Schema Associations: Links between CSV files and their schemas
- Validation Cache: Cached validation results
- User Preferences: Application settings and preferences
- Saved Searches: Any saved search configurations
- Command History: Undo/redo command history
How to Reset the Database
- Navigate to Settings in the left sidebar
- Locate the Database Management section
- Click the "Reset Database to Default" button
- Read the confirmation dialog carefully
- Type
RESETin the confirmation field - Click "Reset Database" to confirm
When to Use Database Reset
Consider using database reset in these situations:
- Fresh Start: You want to start over with a clean slate
- Troubleshooting: Resolving persistent issues with file references or cached data
- Data Cleanup: Removing references to files that no longer exist
- Testing: Resetting the application state for testing purposes
- Privacy: Clearing all application metadata before sharing your computer
After Reset
After a successful database reset:
- The application returns to the landing page
- All metadata is cleared from IndexedDB
- You'll need to re-open your CSV and schema files
- File associations will need to be recreated
- Preferences will return to defaults
💡 Multi-Tab Consideration
If you have CSV Workbench open in multiple browser tabs, close all other tabs before performing a database reset. The reset operation may be blocked if the database is in use by another tab.
✓ Safety Guarantee
Database reset is a safe operation. Your actual CSV and schema files stored on your computer's file system are never touched. Only the application's internal metadata stored in the browser's IndexedDB is cleared.
Best Practices
Follow these best practices for optimal results with CSV Workbench.
CSV File Preparation
- Use comma delimiters: Ensure your CSV uses commas, not tabs or semicolons
- Include headers: First row should contain column names
- Consistent columns: All rows must have the same number of fields
- Proper quoting: Use double quotes for fields containing commas or newlines
- UTF-8 encoding: Save files in UTF-8 encoding for best compatibility
Schema Design
- Start with auto-generation: Let CSV Workbench detect types automatically, then refine
- Add descriptions: Document each column's purpose for future reference
- Use appropriate types: Choose the most specific data type (e.g., MONEY instead of DECIMAL for currency)
- Set realistic constraints: Avoid overly restrictive rules that may reject valid data
- Version your schemas: Increment version numbers when making changes
Validation Workflow
- Validate early: Check CSV structure before creating schemas
- Test schemas: Use "Validate Schema" before applying to CSV files
- Review errors carefully: Each error includes row/column location and suggested fixes
- Fix systematically: Address errors by type or column for efficiency
- Re-validate after changes: Confirm fixes resolved the issues
File Organization
- Use descriptive names: Name files and schemas clearly (e.g., "customer-data-2025.csv")
- Add metadata: Use description and notes fields for context
- Associate schemas: Link schemas to CSV files for quick validation
- Keep schemas with data: Store schema files in the same directory as CSV files
Performance Tips
- Close unused tabs: Free up browser memory for better performance
- Use supported browsers: Chrome 86+ or Edge 86+ on laptop/desktop
- File size awareness: Files ≤50MB are fully editable; >50MB show read-only preview
- Offline capability: Works completely offline with PWA Service Workers
- Local processing: All validation happens in your browser
Architecture
CSV Workbench is built with modern web technologies for maximum performance and security.
Technology Stack
Frontend
- React 19
- TypeScript
- Ant Design v5
- Vite (build tool)
State Management
- Command Pattern (undo/redo)
- IndexedDB (persistence)
Validation Engines
- WebAssembly-powered validation
- Basic CSV validation
- Schema validation
- CSV + Schema validation
- Schema generation
Storage & Files
- File System Access API
- IndexedDB (metadata only)
- Service Workers (PWA)
Key Architectural Principles
- Offline-Capable: All functionality works without internet connection
- Privacy by Design: No data transmission to servers
- Progressive Enhancement: PWA capabilities for installable app experience
- Performance Optimization: Web Workers for background processing, lazy loading for code splitting
- Memory Efficiency: Streaming validation for large files, chunked processing
Data Flow
- User selects CSV file via File System Access API
- File reference (not content) stored in IndexedDB
- File content read on-demand from local file system
- Validation runs in Web Worker with WASM engines
- Results displayed in UI, cached for performance
- Edits saved directly to local file via File System Access API
Validation Engines
CSV Workbench uses specialized WebAssembly validation engines for high-performance data validation.
💡 Validation Architecture
All validation behavior is optimized for deterministic, high-performance operation. Validation rules are defined in schemas, and processing happens locally using Web Workers.
1. validate-basic-csv
Validates CSV structure without a schema. Ensures RFC 4180 strict compliance:
- Comma delimiter only (no tabs or other delimiters)
- Double quote character for field quoting
- Double-quote escaping (no backslash escaping)
- Consistent column counts across all rows
- Proper quote pairing and escaping
2. validate-basic-schema
Validates schema structure before use. Checks:
- Required metadata fields (name, version)
- Valid column definitions
- No duplicate column names
- Constraint logic consistency
- Meta schema compliance
3. validate-csv-schema
Validates CSV data against schema rules. Performs:
- Data type validation for each cell
- Required field presence checks
- Constraint validation (length, range, format, patterns)
- Unique key violation detection
- Cross-field dependency validation
Performance Characteristics
- Memory Efficient: Streaming validation for optimized memory usage
- Background Processing: Runs in Web Worker to keep UI responsive
- Progress Tracking: Real-time progress updates during validation
- Offline-Capable: Works completely offline with PWA capabilities
- Local Processing: All validation happens in your browser with no uploads
- File Editing: Files ≤50MB fully editable; >50MB read-only preview with full validation
RFC 3339 Compliance
CSV Workbench provides full RFC 3339 compliance for datetime validation when using the ISO8601_DATETIME_OFFSET format.
✓ Full RFC 3339 Compliance
The ISO8601_DATETIME_OFFSET variant uses
RFC 3339-compliant parsing functions,
ensuring strict RFC 3339 compliance for Internet protocol interoperability.
What is RFC 3339?
RFC 3339 is an Internet standard (published by IETF) that defines a strict profile of ISO 8601 specifically for use in Internet protocols. It restricts ISO 8601 to a specific subset of formats to ensure better interoperability across systems.
RFC 3339 Format Specification
RFC 3339 defines the following strict format:
date-time = full-date "T" full-time
full-date = date-fullyear "-" date-month "-" date-mday
full-time = partial-time time-offset
partial-time = time-hour ":" time-minute ":" time-second [time-secfrac]
time-offset = "Z" / time-numoffset
time-numoffset = ("+" / "-") time-hour ":" time-minuteValid Examples:
2024-01-15T10:30:00Z(UTC)2024-01-15T10:30:00+05:00(with timezone offset)2024-01-15T10:30:00.123Z(with fractional seconds)2024-01-15T10:30:00-08:00(negative offset)
RFC 3339 Requirements
- Date Format: Only
YYYY-MM-DDallowed - Time Separator: Only
Trequired (uppercase) - Timezone: Only
Zor±hh:mmformat - Full Precision: Complete date and time required (no reduced precision)
- Fractional Seconds: Optional but must use period (.) as separator
- Case Sensitivity:
TandZmust be uppercase
RFC 3339 vs ISO 8601
RFC 3339 is a strict subset of ISO 8601:
✓ RFC 3339 Accepts
2024-01-15T10:30:00Z2024-01-15T10:30:00+05:002024-01-15T10:30:00.123Z
✗ RFC 3339 Rejects
2024-01-15(date only)2024-01-15T10:30:00(no timezone)2024-01-15 10:30:00Z(space separator)2024-01-15T10:30:00+05(incomplete offset)
💡 When to Use RFC 3339
Use the ISO8601_DATETIME_OFFSET variant (RFC 3339 compliant) when:
- Exchanging data with Internet protocols and APIs
- Ensuring strict interoperability across distributed systems
- Working with JSON APIs that expect RFC 3339 timestamps
- Storing timezone-aware timestamps for international applications
Implementation Details
CSV Workbench implements RFC 3339 compliance through:
- RFC 3339 Parsing: Uses standards-compliant parsing for validation
- WebAssembly Compilation: High-performance validation in the browser
- Strict Validation: Rejects any non-RFC 3339 compliant timestamps
- Comprehensive Testing: 100% test coverage for RFC 3339 edge cases
⚠️ Other DateTime Variants
The other datetime variants (ISO8601_DATE,
ISO8601_DATETIME, ISO8601_DATETIME_UTC)
are ISO 8601 compatible but not RFC 3339 compliant. They provide broader
format flexibility for use cases that don't require strict Internet protocol compliance.
Reference
For the complete RFC 3339 specification, see:
RFC 4180 (RFC4180) Compliance
CSV Workbench strictly adheres to RFC 4180 (also written RFC4180), the standard specification for CSV files.
RFC 4180 Requirements
- Delimiter: Comma (,) only - no tabs, semicolons, or other delimiters
- Quote Character: Double quote (") only
- Quote Escaping: Double-quote style ("") - no backslash escaping
- Line Endings: CRLF (
\r\n) per RFC 4180 standard; CSV Workbench also accepts LF (\n) as an enhancement for cross-platform compatibility - Header Row: Optional first row containing column names
- Consistent Columns: All rows must have the same number of fields
💡 Line Ending Enhancement
RFC 4180 specifies CRLF (\r\n) as the standard line ending. CSV Workbench extends this specification to also accept LF (\n) line endings for better cross-platform compatibility with Unix/Linux/macOS systems. CR-only (\r) line endings are not supported.
💡 Why RFC 4180?
RFC 4180 provides a standardized, unambiguous format that ensures maximum compatibility across different systems and tools. By enforcing strict compliance, CSV Workbench eliminates common CSV parsing issues.
What's Not Supported
- Tab-separated values (TSV)
- Semicolon or pipe delimiters
- Single-quote field quoting
- Backslash escape sequences
- Variable column counts per row
Data Privacy
For complete information about data privacy, what data we collect, how we use it, and your privacy rights, please see our Privacy Policy.
GDPR Compliance
For complete information about GDPR compliance and data handling, please see our Privacy Policy.
CSV Troubleshooting Guide
This guide documents common issues encountered when working with CSV files and how CSV Workbench helps prevent, detect, and resolve them.
How CSV Workbench Helps
CSV Workbench is specifically designed to address and prevent many common CSV issues through its built-in validation and security features:
- Automatic Format Validation: When you add a CSV file, it's automatically validated for RFC 4180 compliance, catching structural issues immediately
- UTF-8 Encoding Validation: Built-in encoding validation detects non-UTF-8 characters during the initial file quality check
- CSV Injection Protection: Enterprise-grade security features automatically detect and flag potentially dangerous patterns
- Consistent Column Count Enforcement: RFC 4180 strict compliance ensures all rows have the same number of columns
- Quote Character Validation: Proper RFC 4180 quote handling (double-quote escaping only, no backslash)
- Line Ending Support: Accepts CRLF (RFC 4180 standard) and LF (CSV Workbench enhancement); CR-only not supported
- Browser-Based Editing: Edit CSV files directly in CSV Workbench to avoid spreadsheet application corruption
- File Size Handling: Files ≤50MB are fully editable; files >50MB show read-only preview with full validation
✓ Key Benefit
By using CSV Workbench for all CSV file operations, you can prevent many of these issues from occurring in the first place, rather than having to diagnose and fix them after the fact.
Common CSV Issues and Solutions
1. Spreadsheet Application Data Corruption
Problem: Editing CSV files with spreadsheet applications (Microsoft Excel or Mac Numbers) introduces data corruption that can be difficult to detect.
Common Issues:
- Scientific Notation Conversion: Spreadsheets automatically convert large numeric values (e.g.,
123456789012becomes1.23457E+11) - Leading Zero Removal: Spreadsheets strip leading zeros (e.g.,
00123becomes123), problematic for ZIP codes and account numbers
How CSV Workbench Prevents This: Provides browser-based CSV editor that preserves exact data values without automatic type conversion. Maintains leading zeros and prevents scientific notation conversion. Direct file editing via File System Access API with auto-save.
2. Embedded Commas in Numeric Fields
Problem: Numeric values containing embedded commas (thousands separators) cause parsing failures.
Example Error: strconv.ParseFloat: parsing "2,461": invalid syntax
Why It Fails: CSV Workbench enforces RFC 4180 strict compliance, which requires comma delimiters for field separation only.
Solutions:
- Remove thousands separators:
2,461→2461 - Quote the field:
2,461→"2,461"(treats as string)
How CSV Workbench Detects This: Automatic RFC 4180 validation detects embedded commas in unquoted numeric fields during initial file quality check.
3. Incompatible Line Ending Characters
Background: Different operating systems use different line endings:
- Windows/DOS: CRLF (
\r\n) ✅ Supported (RFC 4180 standard) - Unix/Linux/macOS: LF (
\n) ✅ Supported (CSV Workbench enhancement) - Legacy Mac (pre-OS X): CR (
\r) ❌ NOT supported
RFC 4180 Note: RFC 4180 specifies CRLF (\r\n) as the standard line ending. CSV Workbench extends this to also accept LF (\n) for better cross-platform compatibility, but CR-only (\r) is not supported.
Problem: Files using CR-only line endings are treated as a single line and fail to load.
Solution: Open the file in a text editor (VS Code, Notepad++, etc.) and save it. The editor will automatically convert CR to CRLF.
How CSV Workbench Detects This: Automatic validation checks line ending compliance. Files with CR-only line endings fail the initial file quality check with a clear error message.
4. Non-UTF-8 Characters
Problem: CSV files containing non-UTF-8 characters cause parsing failures with vague error messages.
Detection Command (macOS/Linux):
grep -axv '.*' YourFile.csvRepair Command:
iconv -f utf-8 -t utf-8 -c YourFile.csv > YourFile-clean.csvHow CSV Workbench Detects This: Built-in UTF-8 encoding validation as part of enterprise-grade security features. Automatic detection during initial file quality check with immediate rejection and clear error messages.
5. Inconsistent Column Counts
Problem: CSV files with rows containing different numbers of columns violate RFC 4180 compliance.
Example Error: Row 47: Expected 12 columns but found 11
Common Causes:
- Missing trailing commas on rows with empty final columns
- Extra commas accidentally inserted in data
- Unquoted fields containing line breaks
- Copy-paste errors when manually editing
How CSV Workbench Detects This: Automatic validation when adding a CSV file with precise error reporting showing exact row number and expected vs. actual column count.
6. Missing or Malformed Headers
Problem: CSV files without proper headers or with duplicate column names cause validation failures.
RFC 4180 Requirements:
- First row should contain column names (header row)
- Column names must be unique
- Column names cannot be empty
- Column names should not contain leading/trailing whitespace
How CSV Workbench Detects This: Validates header requirements during initial file quality check and verifies header presence, uniqueness, and non-empty column names.
7. Quote Character Issues
Problem: Improperly escaped or unmatched quote characters cause parsing failures.
RFC 4180 Quote Rules:
- Fields containing commas, line breaks, or quotes must be enclosed in double quotes
- Double quotes within a field must be escaped by doubling them (
"") - No other escape character (like backslash) is valid
Examples:
- Unescaped quotes:
John "Johnny" Doe→"John ""Johnny"" Doe" - Invalid backslash escaping:
"John \"Johnny\" Doe"❌ →"John ""Johnny"" Doe"✅
How CSV Workbench Enforces This: Strictly enforces RFC 4180 quote rules. Only double quotes (") valid for field quoting. Backslash escaping (\") is invalid and rejected.
8. File Size and Performance Issues
Problem: Very large CSV files may cause performance issues or exceed browser memory limits.
CSV Workbench File Handling:
- Files ≤50MB: Fully editable (edit cells, add/delete rows and columns)
- Files >50MB: Read-only preview (first 200 rows displayed)
- Validation: Runs on complete file regardless of size
Performance Tips:
- Close unnecessary browser tabs to free memory
- Use Chrome 86+ or Edge 86+ for best performance
- Ensure adequate system RAM (8GB+ recommended for large files)
- Let validation complete without interrupting
9. Special Characters and Encoding Issues
Problem: Special characters, emojis, or non-standard encoding can cause display or validation issues.
CSV Workbench Requirements:
- Encoding: UTF-8 only
- BOM: Byte Order Mark (BOM) is optional but supported
- Special Characters: All valid UTF-8 characters are supported (including emojis)
How CSV Workbench Handles Encoding: UTF-8 only encoding requirement with BOM support. Built-in UTF-8 validation during initial file quality check detects invalid UTF-8 sequences with clear error messages.
10. CSV Injection Security Issues
Problem: CSV files containing formulas or commands can pose security risks when opened in spreadsheet applications.
What is CSV Injection?
Malicious data starting with special characters can be executed as formulas in spreadsheet applications: = (formula), + (formula), - (formula), @ (formula), | (pipe command)
Example Attack:
Name,Email,Notes
John Doe,john@example.com,=1+1
Jane Smith,jane@example.com,=cmd|'/c calc'!A1How CSV Workbench Protects Against CSV Injection: Built-in CSV injection protection as part of enterprise-grade security features. Pattern recognition detects fields starting with dangerous characters and provides clear warnings.
Quick Reference Table
| Issue | Symptom | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheet Data Corruption | Scientific notation, missing leading zeros | Use CSV Workbench editor, not spreadsheets |
| Embedded Commas | Parse errors on numeric values | Remove thousands separators or quote fields |
| Line Ending Issues | File treated as single line | Save in text editor to fix line endings |
| Non-UTF-8 Characters | Vague parsing errors | Use iconv command to clean file |
| Inconsistent Column Counts | Row has wrong number of columns | Add/remove commas, quote line breaks |
| Missing/Malformed Headers | Duplicate or empty column names | Add unique header row |
| Quote Character Issues | Unmatched or improperly escaped quotes | Use double-quote escaping ("") |
| File Size Issues | Slow performance, memory errors | Use read-only mode for files >50MB |
| Encoding Issues | Garbled characters, wrong encoding | Convert to UTF-8 encoding |
| CSV Injection | Security risk from formulas | Validate with CSV Workbench first |
Recommended Workflow
By making CSV Workbench your primary tool for CSV operations, you transform reactive troubleshooting into proactive prevention:
- Always add CSV files to CSV Workbench first - automatic validation catches issues immediately
- Use CSV Workbench for editing - avoid spreadsheet application corruption
- Generate schemas from data - create validation rules automatically
- Validate before sharing - ensure files are RFC 4180 compliant
- Review validation reports - fix issues with clear, actionable guidance
💡 Still Having Issues?
If you continue to experience problems:
- Try using Database Reset to clear all metadata
- Clear your browser cache and cookies
- Ensure you're using the latest version of Chrome or Edge
- Contact us at hello@csvworkbench.com
Q&A: Common CSV Workbench Use Cases
Real-world scenarios showing how CSV Workbench solves common data quality challenges.
Q1: Manual CSV File Review and Validation
Scenario:
We receive CSV files from external entities and internal groups through manual file transfer processes (email, file share, etc.). We review the files manually, and they often have structural or data corruption issues.
Question:
How can CSV Workbench help with this?
Answer:
CSV Workbench provides immediate validation when you add a CSV file, automatically detecting structural issues, RFC 4180 compliance violations, encoding problems, and security risks. The browser-based editor (for files ≤50MB) lets you fix issues directly without risking spreadsheet application corruption. You can also generate a schema from the CSV file to establish validation rules for future files.
Q2: Automated CSV File Transfer with Data Quality Issues
Scenario:
We receive CSV files from external entities and internal groups via recurring automated file transfers. The files often have structural or data corruption issues that break our file ingestion and processing jobs.
Question:
How can CSV Workbench help with this?
Answer:
CSV Workbench can act as a validation gateway in your automated workflows. First, use the free web application to generate a CSV Schema from a sample file that defines the expected structure and data types. Then, integrate the server-side validation engines (AWS or Azure) into your ETL pipeline to automatically validate incoming files before processing. Files that fail validation are rejected with detailed error reports, protecting your downstream systems from bad data.
Q3: Establishing Clear CSV Data Transfer Standards
Scenario:
We are establishing a new recurring CSV data transfer process and want to define what a properly formatted file looks like to remove any ambiguity.
Question:
How can CSV Workbench help with this?
Answer:
CSV Workbench helps you create a formal data contract using CSV Schema. Generate a schema from a sample file or create one from scratch using the schema editor. The schema serves as executable documentation that clearly defines required columns, data types, validation rules, and constraints. Share this schema with data providers so they know exactly what format is expected. Data providers can then use CSV Workbench themselves to validate their files before sending, ensuring compliance with your requirements. The schema eliminates ambiguity and provides a machine-readable specification that both parties can validate against.
💡 More Questions?
For additional help, see the CSV Troubleshooting Guide or contact us at hello@csvworkbench.com.